Fatigue Area 4. Activity/rest と and 3. Energy balance 00000065 <Definition> Conditions in which daily physical and mental work ability is reduced due to extreme continuous weakness <risk factors> Physical factors, anemia, anticancer therapy or radiation therapy

Nursing diagnosis: fatigue associated with sleep disorders

Nursing diagnosis: fatigue associated with sleep disorders

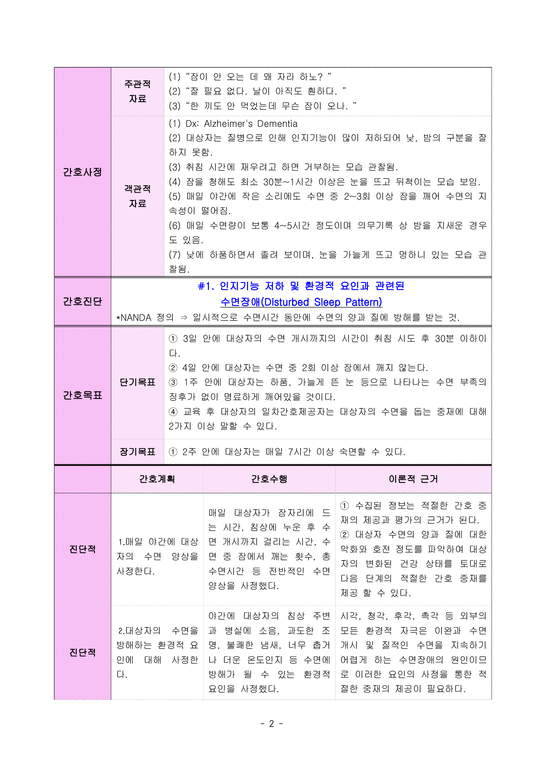
Nurse assessment Subjective data – “I can’t sleep well” – “I don’t think I slept deeply” – “I can’t sleep at night” – “I didn’t eat much” Goal data – wake up at night – I yawn a lot. – Increased need for sleep and rest – Lack of participation in daily activities – Prescription zolpid tab. The Tritico Tab.nurse’s diagnosis fatigue associated with sleep disorders Nursing Plan Desired outcome <long term plan> 1. The patient sleeps without medication within seven days. The patient verbalizes that within three weeks they will be less tired or less tired.<Short-term plan> 1. Patients can identify the cause of fatigue within three days. Patients show increased involvement in daily activities within five days. Patients name nursing interventions (with rationale) that exacerbate and improve fatigue symptoms within three days.Regarding Rationale1 nursing interventions. Ask about the characteristics of fatigue. – Patients feel the most tired during the day. – Factors that exacerbate fatigue – factors that help improve fatigue symptoms – can increase fatigue levels from 0 to 10 – Ability to perform daily tasks – Concentration 1. This information allows nurses to identify patterns. Knowing the nature of fatigue can help you develop a separate care plan. 2. Possible causes of fatigue. Fatigue can be caused by physical, mental, or emotional stressors. Knowing the exact reason and contributing factors can help you plan your care. 3. Observe the patient’s vital signs. Fatigue symptoms may appear in the patient’s vital signs and become more pronounced as fatigue worsens. I advise you to get enough sleep regularly for about eight hours a day. Good quality sleep is essential because it recovers from fatigue during sleep. Conversely, lack of sleep can cause fatigue. Limit to environmental stimuli, especially planned times for rest and sleep. Bright lighting, noise, visitors, a lot of distractions and litter in the patient’s physical environment can limit relaxation, interfere with rest or sleep and cause fatigue. A prescribed medicine (zolpidem tablet) 6 is administered. 7. Relieve the patient’s insomnia. Get comfort from smart touches, massages and a cold shower.7. These may reduce the neural energy that leads to tension relief. 8. Promote adequate nutrition. Patients need an appropriate balanced intake of fat, carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins and minerals to provide energy resources. It helps patients develop habits to promote effective rest/sleep patterns. Promoting pre-sleep relaxation and providing several hours of uninterrupted sleep can contribute to energy recovery.1. Nursing intervention. I asked about the characteristics of fatigue. 3. I thought about the cause of fatigue. 4. Observe the patient’s symptoms. I advised them to get about eight hours of sleep a day regularly. I restricted environmental stimuli, especially
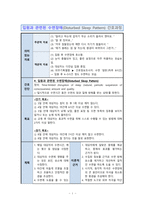
Nurse assessment Subjective data – “I can’t sleep well” – “I don’t think I slept deeply” – “I can’t sleep at night” – “I didn’t eat much” Goal data – wake up at night – I yawn a lot. – Increased need for sleep and rest – Lack of participation in daily activities – Prescription zolpid tab. The Tritico Tab.nurse’s diagnosis fatigue associated with sleep disorders Nursing Plan Desired outcome <long term plan> 1. The patient sleeps without medication within seven days. The patient verbalizes that within three weeks they will be less tired or less tired.<Short-term plan> 1. Patients can identify the cause of fatigue within three days. Patients show increased involvement in daily activities within five days. Patients name nursing interventions (with rationale) that exacerbate and improve fatigue symptoms within three days.Regarding Rationale1 nursing interventions. Ask about the characteristics of fatigue. – Patients feel the most tired during the day. – Factors that exacerbate fatigue – factors that help improve fatigue symptoms – can increase fatigue levels from 0 to 10 – Ability to perform daily tasks – Concentration 1. This information allows nurses to identify patterns. Knowing the nature of fatigue can help you develop a separate care plan. 2. Possible causes of fatigue. Fatigue can be caused by physical, mental, or emotional stressors. Knowing the exact reason and contributing factors can help you plan your care. 3. Observe the patient’s vital signs. Fatigue symptoms may appear in the patient’s vital signs and become more pronounced as fatigue worsens. I advise you to get enough sleep regularly for about eight hours a day. Good quality sleep is essential because it recovers from fatigue during sleep. Conversely, lack of sleep can cause fatigue. Limit to environmental stimuli, especially planned times for rest and sleep. Bright lighting, noise, visitors, a lot of distractions and litter in the patient’s physical environment can limit relaxation, interfere with rest or sleep and cause fatigue. A prescribed medicine (zolpidem tablet) 6 is administered. 7. Relieve the patient’s insomnia. Get comfort from smart touches, massages and a cold shower.7. These may reduce the neural energy that leads to tension relief. 8. Promote adequate nutrition. Patients need an appropriate balanced intake of fat, carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins and minerals to provide energy resources. It helps patients develop habits to promote effective rest/sleep patterns. Promoting pre-sleep relaxation and providing several hours of uninterrupted sleep can contribute to energy recovery.1. Nursing intervention. I asked about the characteristics of fatigue. 3. I thought about the cause of fatigue. 4. Observe the patient’s symptoms. I advised them to get about eight hours of sleep a day regularly. I restricted environmental stimuli, especially